February 24 marked the two year anniversary of the war in Ukraine, starting in 2022 when Russian President Vladimir Putin announced a “special military operation” (code for invasion) of Ukraine in the dawn of February 24th. Russia hoped to take over Kyiv and the country quickly but through Ukrainian resilience, Russian mistakes, and Western aid, Ukraine pushed Russia back.
But now two years later with the counteroffensive in 2023 being a failure and Russia having conquered Avdiivka (having been liberated by Ukraine in 2014 in the early phase of the War in Donbas) and US aid being a deadlock, the war seems to be a slatemate and could be going at Russia favor. So as the war continues with seemingly no end in sight, lets look into the effects that the war had on to Ukraine, Russia, and the world
Ukraine
Remains of a Eastern Orthodox church destroyed during the battle for Donetsk Airport between 2014 and 2015
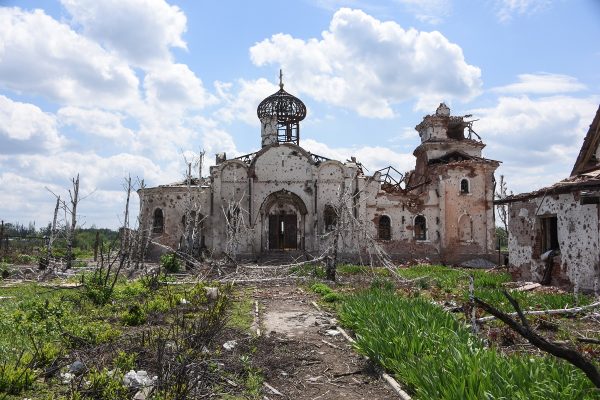

The war has been catastrophic for Ukraine, even before the invasion, Ukraine eastern region the Donbas has been devastated from the eight years of war from 2014 to 2022, the war caused the Donbas which used to be Ukraine’s industrial heartland to dropped 70 percent in the summer 2014, with economic activity in Donetsk Oblast dropping by 38 pecent while Luhansk dropped by 51 percent with a blockade in 2017 further decreasing the region by 20 percent. Beyond just the economy the war also caused the eastern region to become one of the most mine contained regions in the world with a 7,000 square kilometers in government-controlled areas alone are littered with mines and explosives.
The invasion brought the effects from the Donbas to Ukraine nation wide. Poverty soared from 5.5% to 24.2% in 2022 alone with 7.1 million pushed into poverty, Ukraine which is one of the biggest exporters of corps (being known as the breadbasket of the Soviet Union during its Soviet era) is now one of the most food-insecure countries in the world with one in three households now food-insecure, with some areas of Ukraine south and east (where fighting is now concerned) being two in three.
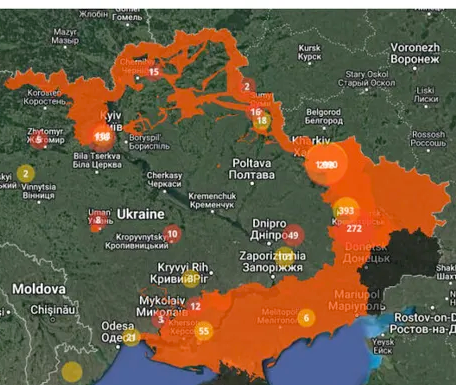
The mines the landmines as of April 2023 covered approximately 174,000 square kilometers of Ukrainian territory (29% to 30%). The war also created whidespread contamination of Ukraine environment with 30% of Ukraine has been contaminated with landmines and unexploded ordnance as well as 30% of protected areas, the destruction of the Kakhovka Dam in 2023 caused up to 1 million people to lose, and submerged 620 square kilometres of territory in four oblasts.
Russia
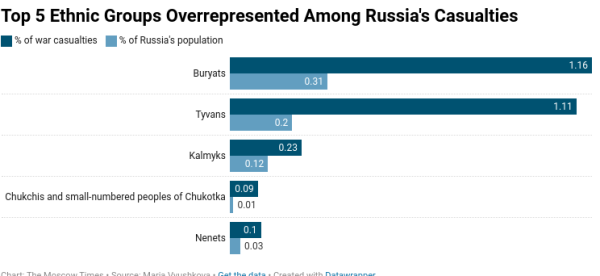
While Russia isn’t as devastated by the war as Ukraine, the war is still hurting Russia in multiple ways, Russia is believed to have lost 66,000 and 120,000 when adding to the number of wounding then the casualties reach to 315,000, Russia lost 8,800 armored vehicles and 20 vessels of its Black Sea fleet have sunk, casualties are worse for ethnic minorities within the Republics of Russia who have been in particular targeted for recruitment and mobilization such as Buryats (a Mongolic ethnicity who are native to southeastern Siberia) amounting to 1.16% of casualities that have been identified despite being 0.3% of Russia population.
A map of the top 5 ethnicities that are overrepresented of Russian casualties in the war

The war has also worsen Russia’s demographic crisis, which was already a issue due to the social upheval when the Soviet Union collapsed resulting in a prevalence of heavy drinking and smoking, poor health care and widespread pollution, it gotten worse with 370,000 Russians fleeing the country during “partial” mobilization in 2022 with some being high as 700,000 among them is the brightest which creating a brain drain for Russia and the lost of younger generations due to dying from the war. Estimates said that Russia’s population which was 146 million when the war begin could decline to 137 to 125 million.
The war also result in the decline of Russia relations with the US and NATO countries (outside of Hungary who leader Viktor Orban has continue close relations with Russia) and with the sanctions a decline with profits from natural gas that India and China are taking advantage of with the discount prices.
Europe
The war has forced Europe to reevaluate it policies on Russia and its militaries especially with the concern of a second Trump presidency due to Trump history with NATO and his comments where he said that countries who didn’t pay their due to NATO (NATO said its members show spend 2% of it GDP on military, something many countries didn’t comply) he allowed them (Russia) to “do whatever the hell they want”.
The war has also brought unity to the EU and NATO where as previously Russia was a polarizing issue for European countries as Northern and eastern-European countries have traditionally pushed for a tougher stance, while western and southern states to press for cooperation even despite Russia illegal annexation of Crimea and its involvement in the War In Donbas which had the EU taking a two-track approach on sanctions and engagement, with the war however the EU have mantained unity despite setbacks such as Hungary attempted to extract concessions and sanction exemptions via the veto power but have failed.
The EU have also reduced its reliance on Russian natural gas and oil and endured the ensuring energy crisis and diversified gas supplies and accelerated the development of renewable energy.
World
The war ripple effects is continuing to affect the world two years on. The war has affected the supply of Ukrainian and Russian grain as the two countries are major suppliers with Ukrainian grain alone in 2021 feeding 400 million people worldwide. The disruption in the supply of grain created a hunger crisis with the rise in food prices, climate change and conflict.
Now multiple countries and regions are at risk of a worsening hunger crisis because of these factors among them are particularity are East Africa which is experiencing the one of its worst droughts in decades the war worsen the growing hunger crisis since 80% of East Africa grain were imported from the two countries with 22 million lacking sufficient and 1.5 million children at risk of malnutrition that is potentially life-threatening. Sri Lanka which was already going through a economic crisis due to unpaid debt and dwindling foreign currency was made worse because of sanctions on Russia and blockade of Ukrainian exports due to the countries be exporters of food, energy and fertilizers and halting its recovery on tourism which declined due to a terrorist attack on 2019 in Easter Sunday, killing 269 people.
The war has also worsen fears of an increase in conflict, especially in the event of a Russian victory in Ukraine which could increase the chance of a war with NATO as some leaders in Europe have raised such as Lithuania not helping is Russia making similar accusations of persecution of Russians and threats on countries like Moldova or Governor of the Russian occupation of Zaporizhzhia Oblast Yevgeny Balitsky saying that all of the Baltics nations were “all our lands, and our people live there” and wanting to correct it by “correct this…through the might of Russian weapons”. Fears also were on the potiential of other countries that have irredentist claims to land being encouraged to act them out with the idea of getting away with it like Russia with a frequently incited example being China and Taiwan or North Korea with South Korea. There also concerns of Russia attacking on nations close to it aside Europe such as Georgia having already occupied Abkhazia and South Ossetia back in 2008 and Northern Kazakhstan due to the sizable Russian population there.
What to expect in the future?
The outcome of the war in the future depends on multiple factors such as the outcome of the 2024 Presidential election and US aid and support coming in which is currently being blocked by the House Republicians and continued support being threatened on the event that Donald Trump comes to power in a second presidency.
As one expert Michael Kofman notes in the start of 2024 for Ukraine “Ukraine starts 2024 in a very difficult position. That is very clear. Ukraine has a deficit in terms of artillery ammunition. Part of that is because it depends on Western support for munitions, and it has a deficit of manpower.”
One thing is certain is the war has no end in sight in part because both sides still believe they can win and both sides see the war as the fight for their existence especially on Ukraine part.
Quoting a leading Russian Expert Angela Stent “Despite all the horrors of this war, the majority of Ukrainians want to continue fighting. The vast majority of them say that they will continue fighting until they win because for them, this is really a war of independence. This is a war for their existence,”
One thing that all experts agree was a ceasefire would only make things worse especially when looking at the history in the Donbas War, where Russia violated ceasefires from the Minsk I and II agreements to take advantage of Ukraine weaken state to conquer more territory such as Debaltseve.
As the Head of Eastern Europe Programme Daniel Szeligowski puts it “Putin will get no rest until he either subjugates Ukraine or destroys it. This imperial self-conception is not just his, but that of Russian elites at large. What happens in Ukraine will not stay in Ukraine. Russia’s long-term strategic goal is to bring back its global power status and recreate a security order built on spheres of influence, and it will not shy away from deploying people and resources from conquered Ukraine against the West.”
Sources:
https://neweasterneurope.eu/2019/09/24/the-cost-of-five-years-of-war-in-donbas/
https://www.rescue.org/uk/article/ukraine-war-what-are-impacts-world-today
https://www.rand.org/pubs/commentary/2023/02/consequences-of-the-war-in-ukraine-a-bleak-outlook.html
https://www.usip.org/publications/2024/03/ukraine-war-takes-toll-russia







